Getting R up and running
We want to accomplish two things here: first, install the latest version of R and second, install RStudio, which is an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) for R.
Let's start by going to R's homepage at https://www.r-project.org/. This page will look similar to the following screenshot:
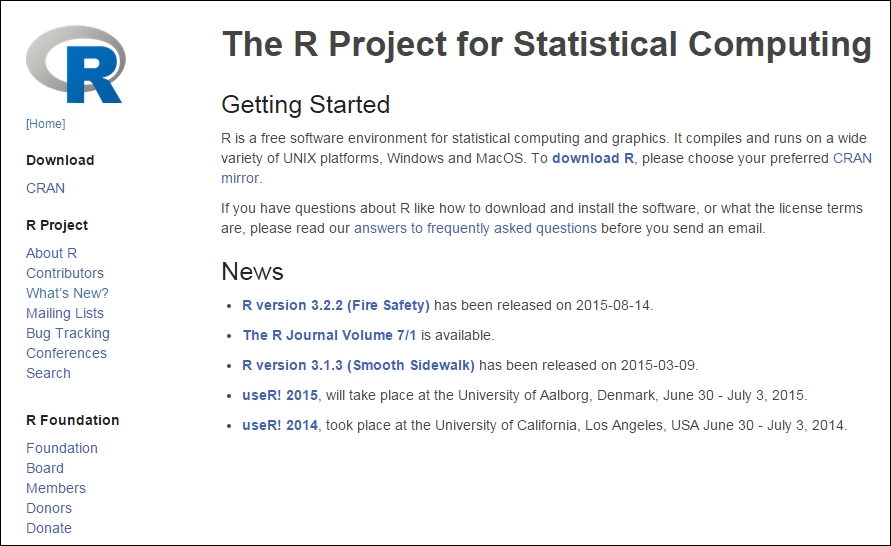
You can see that there is a link, download R, and in the News section, the latest R version is 3.2.2 (Fire Safety), which was released on 2015-08-14. Now, click one of the links, either CRAN under Download or download R under Getting Started, and you will come to the following screen, which has CRAN Mirrors:

These are the links by country and sorted alphabetically that will take you to the download page. Being in Indiana, USA, I will scroll down and find that Indiana University has a link:

Once you find a similar link that is close to your location, click on it and you will see this as part of the page that will be loaded:
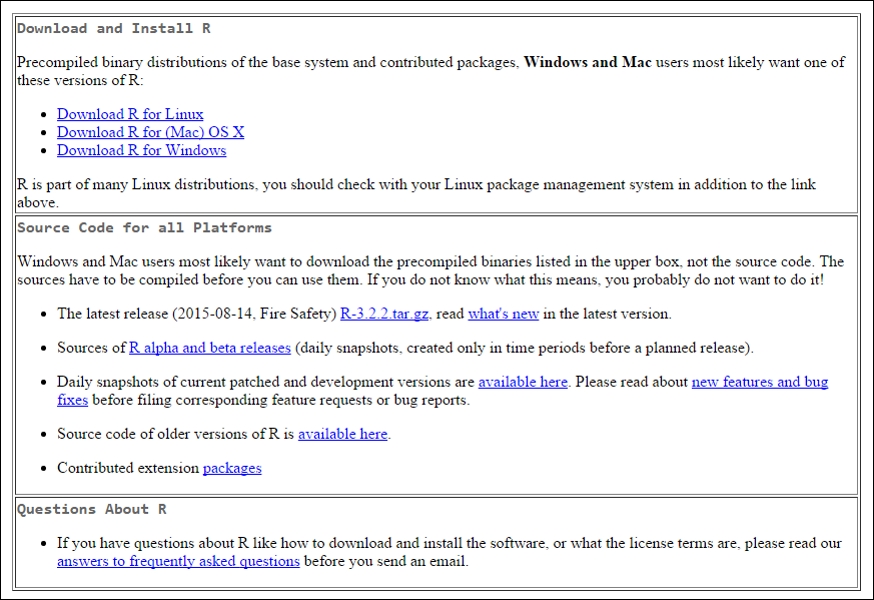
Now, click on your appropriate operating system:
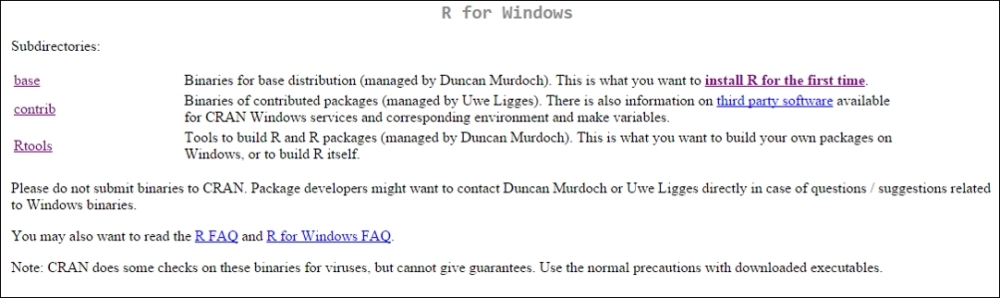
What we want now is to install base R for the first time, so click install R for the first time and we will come to the following page that will initiate the download:
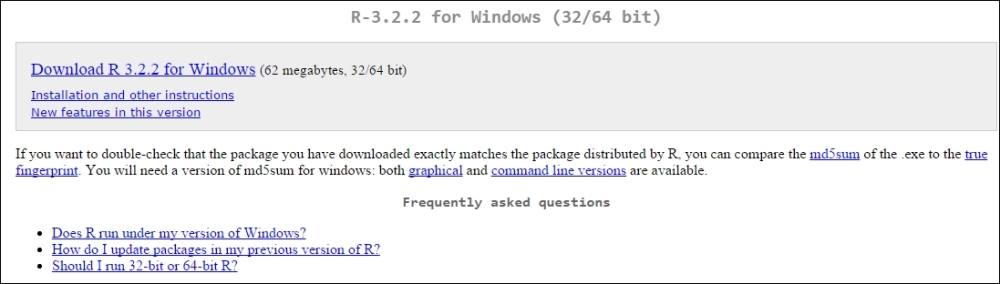
Now, you can just download and install R as any other program. After the installation, run R and you will see the base Graphical User Interface (GUI):
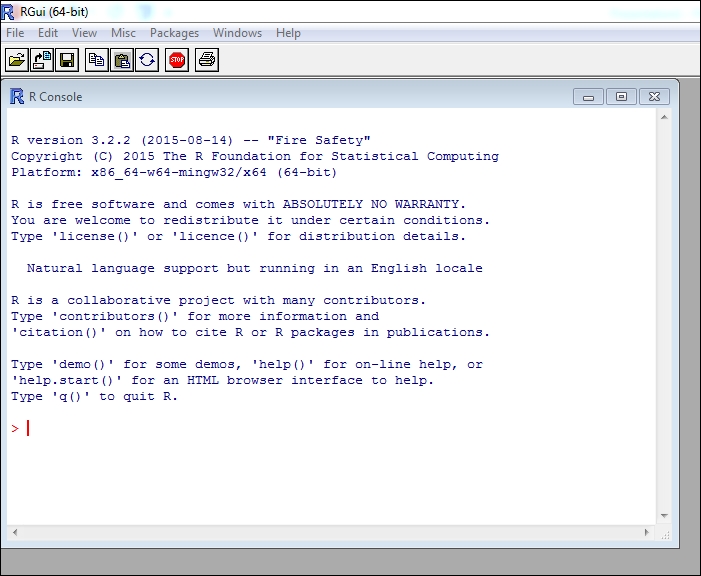
This is all you need to run all of the code in this book. However, it is extremely helpful if you utilize R in the context of RStudio's IDE, which is available for free. This link will direct you to the page where you can download the free version:
https://www.rstudio.com/products/RStudio/.
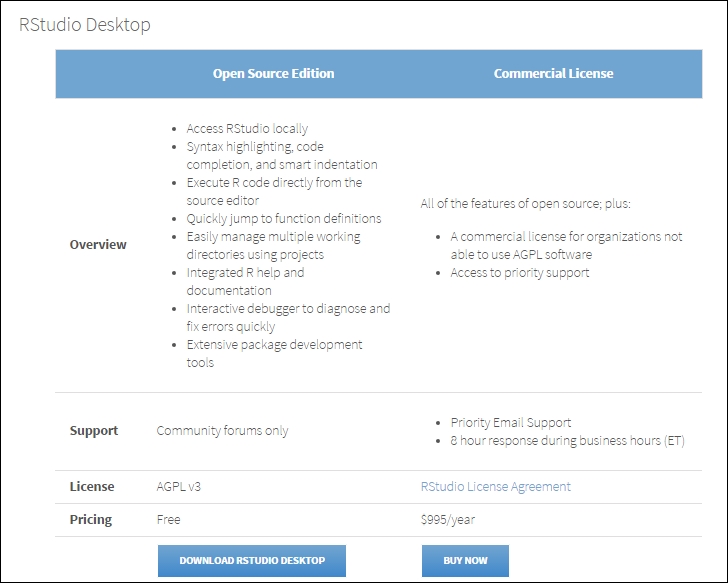
On this page, you will find the download for the free and commercial versions. Needless to say, let's stick with the free version, so download and install it:
After this is installed and opened for the first time, you will see something as the following. Keep in mind that it will be different from what you see here based on the packages that I have loaded and the operating system:
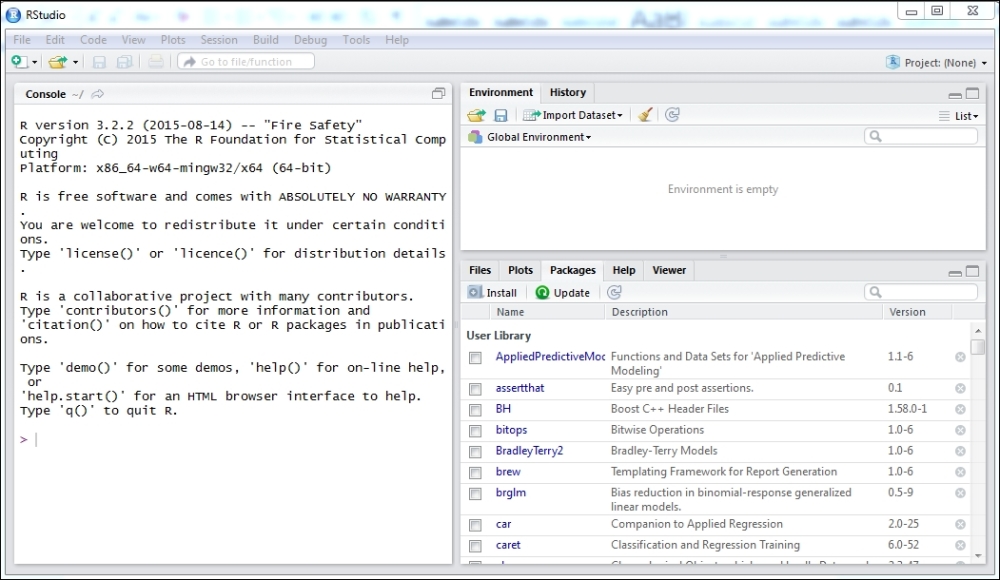
Note that on the left is the same console with the command prompt that you can see in the preceding figure. The IDE improves the experience such that you can manage Environment and History (to the upper right) and Files, Plots, Packages, and Help (to the lower right).
Let's not get distracted here with a full tutorial on what RStudio can do but focus on a couple of important items. One of the great benefits of R is the vast number of high quality packages to various analyses. Let's look at how the IDE ties it all together by loading a package called abc, which stands for approximate Bayesian computation. Go to the command prompt and type the following:
> install.packages("abc")
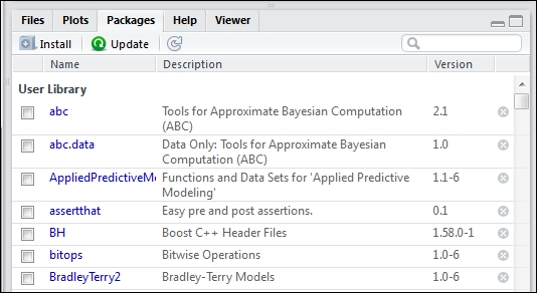
After this runs, notice that in the lower right panel (ensure that the Packages tab is clicked on) that the abc package is now installed as well as the dependent abc.data package:
Now, go to the upper right and click on the History tab. You should see the command that you executed in order to load the package:
Now, if you click on the To Console button, it will be placed in front of the command prompt. If you click To Source, you will see a new area open that will allow you to put your project script together. If you click both the buttons, you will end up with something similar to this output:
The install.packages() command has now gone from the history to a source file. As you experiment with your code and get it to where it works as you want it, put it into a source file. You can save it, e-mail it, and so on. All the code for each of the chapters in this book are saved in a source file.



























































