Understanding queues and queue families
Queues are the means by which an application and a physical device communicate. The application provides the jobs in the form of a command buffer that is submitted to the queues. These are read by the physical device and processed asynchronously.
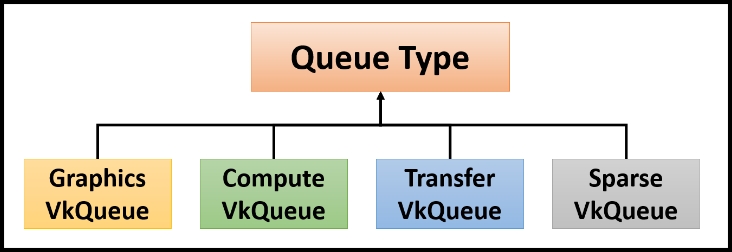
A physical device may support four types of queues, as shown in the following diagram. There could be multiple queues of the same type on a physical device; this allows the application to choose the number of queues and what type of queue it needs. For example, a simple application may require two queues: compute and graphics; here, the former is used for convolution computing and the second renders the computed blur image.
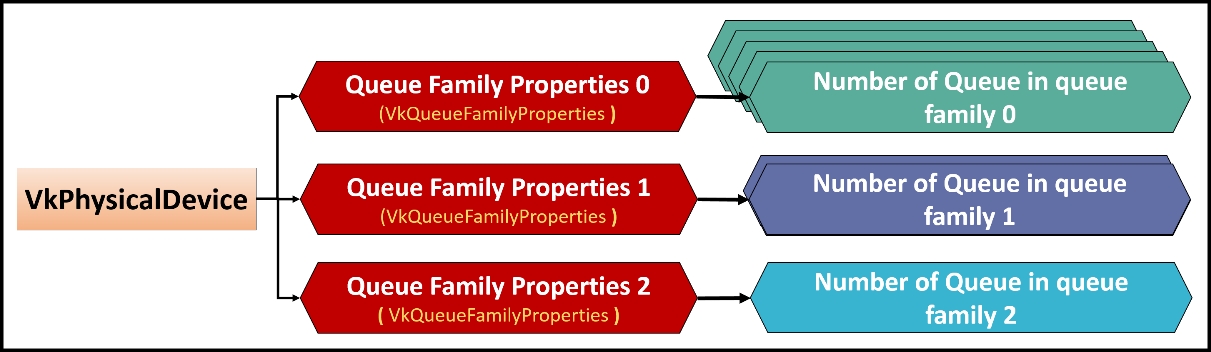
A physical device may consist of one or more queue families exposing what types of queue exist inside each queue family. Further, each queue family may have one or more queue count. The following diagram shows three queue families with their respective multiple queues: