Data integration made easy – TFDLocalSQL
As Wikipedia says:
"Data integration involves combining data residing in different sources and providing users with a unified view of them."
Traditionally, information must be stored in a single database with a single schema, but many organizations store information on multiple databases, so they need a way to retrieve data from different sources and assemble it in a unified way.
FireDAC provides a component that permits you to execute SQL statements against any dataset: TFDLocalSQL.
Getting ready
Let's imagine that a company wants to gain some business intelligence on their data. The marketing department, to allow special customers to take advantage of a special promotion, wants a list of customers who have spent at least a certain sum in at least one order.
The problem is that customers are provided in XML format and sales are stored in a database table. We want to achieve the aim of executing heterogeneous queries—XML and database tables. Let's go!
Note
Ensure you have followed the instructions in theThe Amazing FDTable recipe on database preparation. If you haven't, go to it and set up your environment.
How to do it...
Let's look at the following steps:
- Create a new VCL application by selecting
File|New|VCL Forms Application. - Put a
TFDConnectionon the form and set itsDriverNametoSQLite(because SQL Local usesSQLLitein its engine).
- Place on the form a
DBEdit(aligned to the top), aTButton(aligned to the top), aDBNavigator(aligned to the top), aDBGrid(aligned to the client), and aDataSource. Set theDataSourceproperty ofDBNavigator1andDBGrid1toDataSource1. - From
DataExplorer, drag and drop onto the form theSALEStable from theDELPHICOOKBOOKconnection under the InterBase voice. - Now, put on the form one
TFDQuery, oneTFDLocalSQL, and oneTClientDataSet. - It's time to rename components:
Old | New |
|
|
|
|
|
|
- If you performed all the steps correctly, you should be in this situation:

Figure 1.33: Form layout at design time
- Set the
FDLocalSQL1connection toFDConnection1. - Select the
DataSetsproperty ofFDLocalSQL1and click the ellipsis button (...) to enter the editor.
- Click the
Add Newbutton on the editor twice to add two datasets to theDataSetscollection. - Select the first dataset in the collection and set the
DataSetproperty toSalesTable; set theNameproperty toSalesin order to use the Sales identifier in SQL to refer to this dataset. - Select the second dataset in the collection and set the
DataSetproperty toCustomersCDS; set theNameproperty toCustomersin order to use the customers identifier in SQL to refer to this dataset:
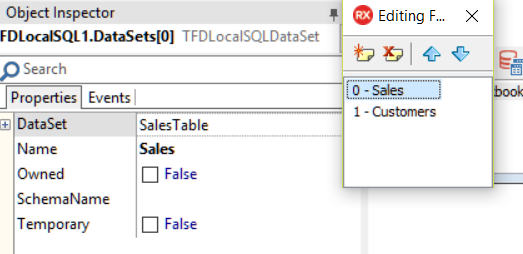
Fig 1.34: FDLocalSQL DataSets editor collection
- In the private section of the form, declare a procedure named
OpenDataSetsand put in the following code:
procedure TMainForm.OpenDataSets; begin SalesTable.Open(); CustomersCDS.Active := True; end;
- In the private section of the form, declare a procedure named
PrepareDataSetsand put in the following code:
procedure TMainForm.PrepareDataSets; begin CustomersCDS.FileName := 'C:\Users\Public\Documents\Embarcadero\Studio\19.0\Samples\Data\customer.xml'; LocalQuery.SQL.Text := 'select distinct c.* from Customers c ' + ' JOIN Sales s on cast (s.CUST_NO as integer) = c.CustNo ' + ' where s.total_value > :v order by c.CustNo '; end;
- Generate a
FormCreateevent handler and put in this code:
procedure TMainForm.FormCreate(Sender: TObject); begin PrepareDataSets; end;
- We have almost finished; now, we need to put everything together. Generate the
Button1 Clickevent handler and put in this code:
procedure TMainForm.btnExecuteClick(Sender: TObject); var LAmount: Integer; begin // ensure amount is an integer ifnot TryStrToInt(Edit1.Text, LAmount) then begin ShowMessage('Amount must be integer...'); exit; end; LocalQuery.Close; OpenDataSets; // apply user data LocalQuery.ParamByName('v').AsInteger := LAmount; // Execute the query through eterogeneous sources LocalQuery.Open; end;
- Run the application by hitting F9 (or by going to
Run|Run).
- Try different amounts to filter the different customers:
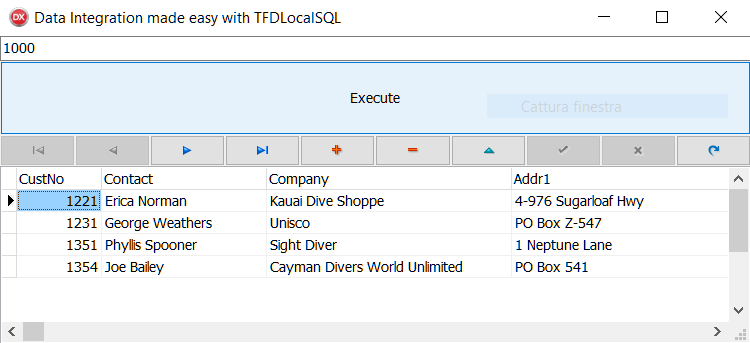
Figure 1.35: Data integration in action
Following image is an example showing different amounts to filter the different customers:
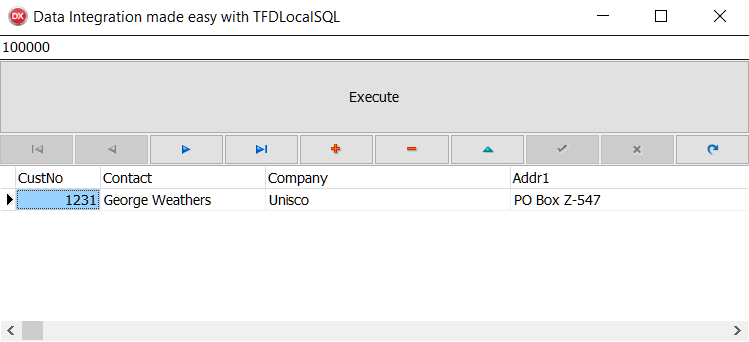
Figure 1.36: Another example of Data integration in action
How it works...
The code of this recipe is quite simple but I want to explain it anyway.
Our data is stored in two different dataset—SalesTable, which refers to a database table, and CustomerCDS, which refers to an XML file. By setting the FDConnection1, FDLocalSQL1, and LocalQuerycomponents as explained in the previous How to do it... section, it is possible to have an FDQuery component (LocalQuery) where we write the query using different heterogeneous sources:
select distinct c.* from Customers c JOIN Sales s on cast (s.CUST_NO as integer) = c.CustNo where s.total_value > :v order by c.CustNo
When you click on the Execute button, preliminary checks are carried out on the validity of the data entered, then the query in LocalQuery is performed and the LocalQuery dataset is populated with data... from heterogeneous sources! This is a really great feature!
There's more...
The Local SQL is based on the SQLite database and supports most of the SQLite SQL dialect.
All the read and write operations are performed through the TDataSet API with some extensions, which means that FireDAC performs the operations by converting SQL into dataset calls. This is the reason why you can execute SQL statements against any dataset—FDQuery, IBQuery, ClientDataSet, third-party components, and so on.
The possible applications of Local SQL are (from Embarcadero DocWiki):
- Heterogeneous queries: Queryable datasets have result sets from different DBs
- In-memory database:
TFDMemTablesserve the datasets - Advanced offline mode: In this case, although the main DB is not accessible, an application is still able to perform SQL queries
- Advanced DataSnap client: The data delivered by the
DataSnapdriver to the client can be queried locally - Simplified migration: A developer can use the third-party
TDataSetobjects in an application, and can use a FireDAC API to work with these data sources
Here some important notes (from Embarcadero DocWiki):
- The Local SQL engine does not support datasets with multiple result sets.
- The Local SQL engine supports the
INSERT/UPDATE/DELETESQL commands as transactions and savepoints. Also, it transforms the corresponding SQL commands intoTDataSetAPI calls. - The Local SQL engine supports
INSERT/REPLACE, but uses only primary key fields to find a record to replace when a primary or unique key constraint is violated. Additionally, when only several fields are specified inINSERT/REPLACE INTO tab (<field list>), the fields that are not specified get null values on updating. - The Local SQL engine uses the
TDataSetAPI with some extensions provided by theIFDPhysLocalQueryAdapterinterface. FireDAC datasets implement this interface. Optionally, for non-FireDAC datasets, a developer can create a class implementing the interface and assign its instance to theTFDLocalSQL.DataSets[..].Adapterproperty.
See also
- For more information, take a look at http://docwiki.embarcadero.com/RADStudio/en/Local_SQL_(FireDAC)































































